Çocuk Kalp Hastalıkları ve Cerrahisi (Pediatric Heart Diseases and Cardiac Surgery)
Çocuk Kalp Cerrahisi Platformu (Platform for Pediatric Heart Surgery)
Pediatrik Kalp Hastalıkları ve Cerrahisi
Pediatric Heart Diseases and Cardiac Surgery
Ross operasyonu
Ross Procedure

Pathophysiology
Aortic valve stenosis causes progressive left ventricular hypertrophy with associated sequelae of decreased ventricular function and myocardial ischemia. These factors place the patient at increased risk for sudden death. Aortic valve insufficiency results in left ventricular dilatation, decreased cardiac output and can eventually lead to congestive heart failure. Exercise intolerance and exertional dyspnea can occur in patients with severe forms of aortic valve disease. The Ross procedure is an innovative technique that utilizes the patient's own pulmonary valve for aortic valve replacement. A cryopreserved pulmonary valve homograft is used to replace the patients native pulmonary valve. Intermediate follow-up studies indicate that the pulmonary autograft grows, making the Ross procedure the aortic valve replacement technique of choice for small children and infants. Further, anticoagulation with coumadin is not required following the Ross procedure. In contrast to traditional mechanical aortic valve replacement, however, the Ross procedure is a more extensive operation. In addition, later replacement of the pulmonary valve homograft is generally required due to growth of the patient or degeneration of the homograft.
Surgical Technique
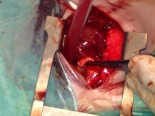
Aortic valve replacement requires cardiopulmonary bypass and aortic cross-clamping. The aorta is opened and the aortic valve is inspected. Once suitability for the Ross procedure has been determined, the pulmonary root autograft is excised. As the aortic root is excised, the coronary artery ostia are excised as buttons with adjacent aortic wall tissue. In children, implantation of the autograft is generally performed as a root replacement. The proximal pulmonary autograft is secured in the position of the native aortic root. The coronary arteries are next implanted, and the distal end of the autograft is anastomosed to the ascending aorta. A cryopreserved, valved pulmonary homograft is inserted in the position of the original pulmonary root. Transesophageal echocardiography is utilized to assess adequacy of the repair. Cardiopulmonary bypass time and aortic cross-clamp time required to complete repair are moderate to long.
Postoperative Considerations
The postoperative course following the Ross aortic valve replacement procedure can be variable. This is an extensive operation and inotropic support is frequently required. Invasive monitors utilized following surgery include arterial, central venous, and left atrial catheters. An oximetric catheter is utilized to assess cardiac output. Vasoactive infusions required for hemodynamic management might include dopamine or dobutamine, epinephrine, milrinone, nitroprusside or phenoxybenzamine, and nitroglycerin. Postoperative bleeding is a potential complication since there are numerous external cardiac suture lines exposed to systemic pressure. Cardiac arrhythmias occasionally occur following repair. Temporary atrioventricular pacing capability should be readily available. Postoperative intracardiac pressures should be normal. Slightly elevated left atrial pressure may occur secondary to left ventricular hypertrophy and poor left ventricular compliance. Arterial oxygen saturation should be normal. Length of hospital stay following the Ross procedure averages one week to ten days.